Solution Pattern: Minimize Downtime when Migrating from Hypervisors to OpenShift Virtualization
Architecture
1. Common Challenges
When moving applications or service across environments, there are a number of common challenges that enterprise organizations must address. Below are some of the common challenges:
-
Minimizing Downtime: Keep downtime to a minimum while maintaining service continuity. Ideally enterprises would prefer to have as little downtime as possible while maintaining service continuity.
-
Reducing Complexity: Reducing the complexity of setting up and managing complex networking systems, such as firewalls and routing, VPNs to connect the older environments to the new ones, during the transition
-
Avoid Application Level Changes: When the services are migrated to the new platform, the applications must be able to communicate with each other using the same service address.
2. Technology Stack
-
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization: Red Hat® OpenShift® Virtualization, provides a modern platform for organizations to run and deploy their new and existing virtual machine (VM) workloads. It allows for easy migration and management of traditional virtual machines onto a trusted, consistent, and comprehensive hybrid cloud application platform. OpenShift Virtualization offers a path for infrastructure modernization and aims to preserve existing virtualization investments while embracing modern management principles.
-
Red Hat Service Interconnect: Red Hat Service Interconnect simplifies application connectivity across the hybrid cloud. Unlike traditional means of connectivity (such as VPNs combined with complex firewall rules), development teams can easily create interconnections across different environments without compromising the organization’s security or data. Applications and services across environments can communicate with each other using Red Hat Service Interconnect as if they were all running in the same site. This connectivity can be maintained even as applications are migrated between environments.
-
Red Hat OpenShift: Red Hat® OpenShift® is a trusted, comprehensive, and consistent platform to develop, modernize, and deploy applications at scale, including today’s AI-enabled apps. Innovate faster with a complete set of services for bringing apps to market on your choice of infrastructure.
3. An in-depth look at the solution’s architecture
Instamedi’s patient portal application consists of 3 key components.
-
Frontend - A web front-end service that uses the PostgreSQL database and a payment processor deployed in a private cluster to display the names of doctors and patients and process the payments.
-
PostgreSQL database - Stores a list of patients, doctors and the bills owed by patients
-
Payment Processor - To process the payments made by the patients and indicate the location (environment) where the payment was processed.
The frontend is deployed on an OpenShift cluster. Both the database and the payment processor are deployed on a VM running of one of the traditional hypervisor platform. Instamedi, wants to migrate all the components from the traditional hypervisor platform to OpenShift virtualization, without having any downtime. Initially there are no components running on OpenShift Virtualization.
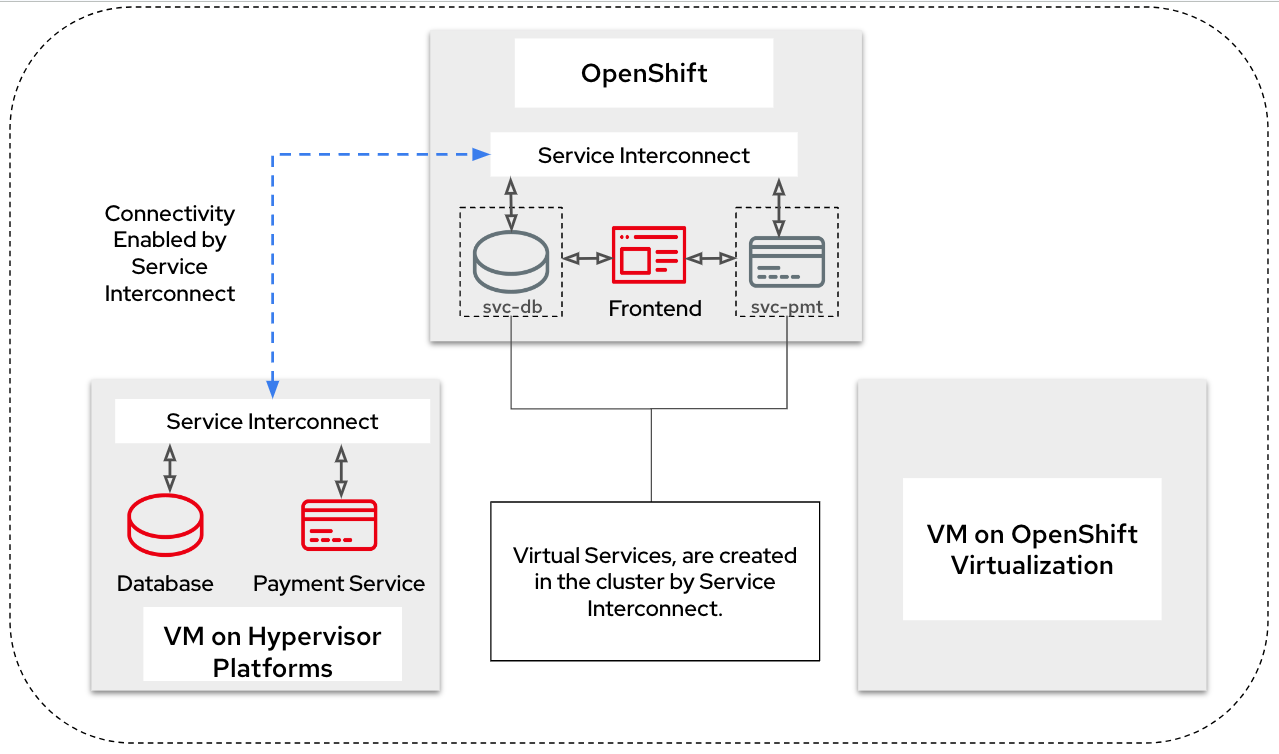
The frontend is connected to the other components on the traditional hypervisor platform through a Virtual Application Network enabled by Red Hat Service Interconnect. Once a service is exposed over network, Service Interconnect router creates a virtual local service in the OpenShift environment. The frontend connects to these services as if they are local services and the router takes care of routing the call to the correct destination. The frontend is not aware of location of the actual services.
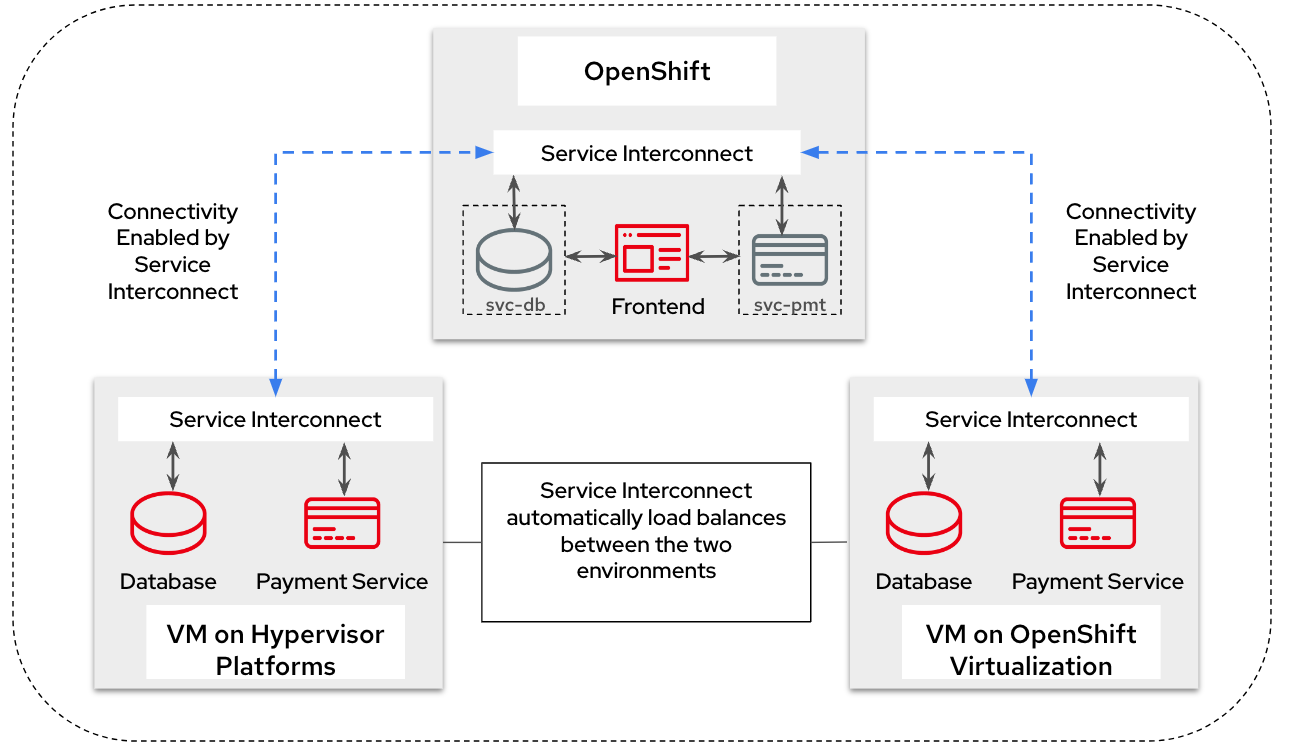
They gradually migrate the components one by one. This is how Instamedi’s environment would look like during the middle of the transitioning stage. All the instances of the database and payment service running on both the hypervisor platform and OpenShift Virtualization, are explicitly given the same service address on the network, so that they point to the same virtual service/proxy on the OpenShift cluster. This also ensures that no changes are made to the frontend since the service name that it refers to remains constant irrespective of where the database and payment processor components are deployed. The anycast capabilities of Service Interconnect ensure that the load is balanced between the two instances. This way Instamedi can have both the environment simultaneously running until they complete all the tests and are sure to decommission the old environment.
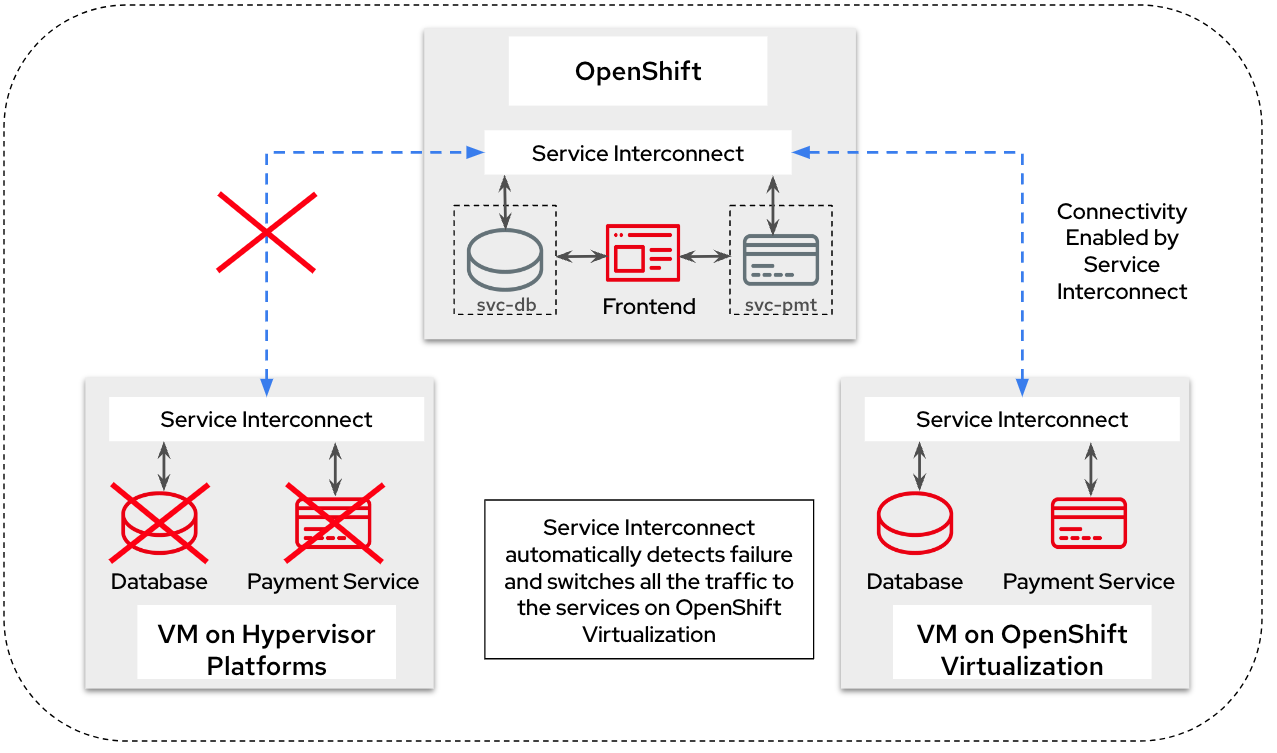
Finally, once the migration team is completely sure that everything is running smoothly, they can decommission the old environment. The network between the Openshift cluster and the traditional hypervisor platform is deleted, using a single command. Once this is done, Service Interconnect automatically reroutes all the traffic to the service running in the OpenShift Virtualization environment. All this is done without making any changes to the frontend, database or the payment processor. In fact, the frontend team doesn’t even realise that a migration has happened, since there was no code change and no downtime.