Solution Patterns: Accelerate time to value with Red Hat Openshift Service on AWS
1. Solution overview
This solution pattern brings an architectural solution demonstrating the integration of Red Hat Openshift Service on AWS(ROSA) with different AWS services.
ROSA(Red Hat Openshift Service on AWS) is a fully-managed, turnkey application platform that allows you to focus on delivering value to your customers by building and deploying applications. Red Hat and AWS Site reliability engineering (SRE) experts manage the underlying platform so you do not have to worry about the complexity of infrastructure management. ROSA provides seamless integration with a wide range of AWS compute, database, analytics, machine learning, networking, mobile, and other services to further accelerate the building and delivering of differentiating experiences to your customers.
2. How ROSA is different from DIY Kuberenetes
Container and Kubernetes are the modern elements of business software success. But it requires training and a great amount of effort to shift to Kubernetes. Let us see how ROSA differs from DIY Kubernetes:
-
ROSA is a Managed Application platform: DIY Kubernetes can be tricky to get it up and running. There are many options and configurations available to customize the Kubernetes clusters as per the requirements. To setup different environments and make those available quickly with strong security posture is no small task. It can take a whole team of people to keep such systems up and running. ROSA provides a higher class of service, support and hosting , along with enhanced securityy capabilities. With Red Hat’s SRE running the infrastructure, Application team can focus on the applications instead of spending time standing up and installing systems so that container workloads can be deployed on those clusters.
-
ROSA provides automation and management: With tools like Ansible, Argo CD and Git, nearly any workflow can be automated into a pipeline. But this level of automation takes time to build and customize, just like any infrastructure. For teams that aren’t yet specialized in the new "cloudy" way of building software abd even for teams that would rather spend their cycles away from infrastructure, Red Hat Openshift Service on AWS features helpful automation tools and processes to help speed up the process. Instead of building your development pipelines from scratch, ROSA can tie in your existing systems and tools, such as GitHub and Ansible. Even better, our SREs have constructed patterns for your developers to use, with pre-configured versions of essential infrastructure ready to go at the drop of a hat.
4. Benefits of ROSA
Organizations are looking for a way to deliver high quality, innovative applications that provide greater business value and effectively scale according to rapidly changing demands. Here are the features & benefits of ROSA:
-
A Native AWS Experience: ROSA enables organizations to take advantage of the power of Openshift, the industry’s leading enterprise Kubernetes platform, as a native AWS service from the AWS Management console.
-
Easier Container Adoption & Cloud Migration: ROSA delivers enterprise-ready Kuberenetes that many companies already use on-premises today, enhancing the ability to shift workloads to the cloud and making it even easier for customers to adopt containers and deploy their applications faster on AWS.
-
Fully Managed Platform: Installation, monitoring, management, maintenance, and upgrades are performed by Red Hat site reliability engineers (SRE) covering the complete stack including the control plane, worker nodes, and key services.
-
Streamlined, integrated support & billing experience: Jointly operated & supported by Red Hat & AWS with an integrated support experience and 99.95% uptime SLA. Customers will also receive a single bill from AWS for both OpenShift & AWS consumption.
-
Maximum availability: Deploy clusters across multiple Availability Zones in supported Regions to maximize availability.
-
Regulatory compliance: Address comprehensive security and compliance needs with industry-specific standards and regulations such as SOC-1, SOC-2 Type 1 & 2 and ISO-27001.
5. Features of ROSA
-
Security:
-
Network Security:
-
Firewall & DDoS protection: Each ROSA cluster is protected by a secure network configuration using firewall rules for AWS Security Groups. ROSA customers are also protected against DDoS attacks with AWS Shield Standard.
-
Private clusters and network connectivity: Customers can optionally configure their ROSA cluster endpoints, such as web console, API, and application router, to be made private so that the cluster control plane and applications are not accessible from the Internet. Red Hat SRE still requires Internet-accessible endpoints that are protected with IP allow-lists. AWS customers can configure a private network connection to their ROSA cluster through technologies such as AWS VPC peering, AWS VPN, or AWS Direct Connect.
-
Cluster network access controls: Fine-grained network access control rules can be configured by customers, on a per-project basis, using NetworkPolicy objects and the OpenShift SDN.
-
-
Compliance: ROSA is currently compliant with SOC-1, SOC-2 type 1 & type 2, ISO-27001, & PCI-DSS. We are also currently working towards FedRAMP High, HIPAA, ISO 27017 and ISO 27018.
-
Vulnerability Management: Red Hat performs periodic vulnerability scanning of ROSA using industry standard tools. Identified vulnerabilities are tracked to their remediation according to timelines based on severity. Vulnerability scanning and remediation activities are documented for verification by third-party assessors in the course of compliance certification audits.
-
STS: ROSA utilizes AWS Security Token Service for all of the AWS IAM roles it uses to reach the AWS API. This allows the platform to address the principle of least privilege in customer accounts. Instead of each cluster requiring a single high-privilege role, each component of the cluster has as a role and policy with the specific permission actions required.
-
-
Availability:
-
High Availability: Installation, monitoring, management, maintenance, and upgrades of clusters are performed by Red Hat site reliability engineers (SRE) covering the complete stack including the control plane, worker nodes and key services. You can also deploy clusters across multiple Availability Zones in supported regions to maximize availability.
-
Joint Support: ROSA is jointly supported by Red Hat and AWS with an integrated support experience and 99.95% uptime SLA. You can either contact AWS support via the Support Center accessible from the AWS console (https://console.aws.amazon.com/support/), or you can open a support case via Red Hat’s Customer Portal (https://access.redhat.com) where you will also find self-service support articles and up to date phone contact information.
-
-
Durability:
-
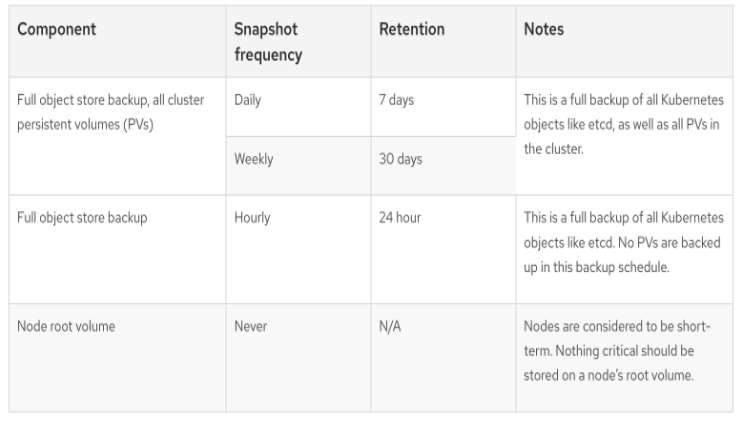
Backup & Recovery: All Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster metadata from OpenShift Cluster Manager is securely backed up by Red Hat. Red Hat does not commit to any Recovery Point Objective (RPO) or Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Customers are responsible for taking regular backups of their data. Customers should deploy multi-AZ clusters with workloads that follow Kubernetes best practices to ensure high availability within a region. If an entire cloud region is unavailable, customers must install a new cluster in a different region and restore their apps using their backup data. The following table outlines backup and recovery strategies:
-
-
Scalability:
-
Autoscaling: Node autoscaling is available on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS. You can configure the autoscaler option to automatically scale the number of machines in a cluster. The cluster autoscaler increases the size of the cluster when there are pods that failed to schedule on any of the current nodes due to insufficient resources or when another node is necessary to meet deployment needs. The cluster autoscaler does not increase the cluster resources beyond the limits that you specify.
Additionally, the cluster autoscaler decreases the size of the cluster when some nodes are consistently not needed for a significant period, such as when it has low resource use and all of its important pods can fit on other nodes. When you enable autoscaling, you must also set a minimum and maximum number of worker nodes.
-
-
Performance:
-
Platform monitoring: Red Hat site reliability engineers (SREs) maintain a centralized monitoring and alerting system for all ROSA cluster components, the SRE services, and underlying AWS accounts. Platform audit logs are securely forwarded to a centralized security information and event monitoring (SIEM) system, where they may trigger configured alerts to the SRE team and are also subject to manual review. Audit logs are retained in the SIEM system for one year. Audit logs for a given cluster are not deleted at the time the cluster is deleted.
-
-
Ease of install and upgrade:
-
Installation: Customers can easily deploy fully managed Red Hat Openshift service in AWS cloud. Red hat has worked closely with Amazon to integrate this service via AWS management console allowing existing amazon customers to onboard Openshift capabilities by a simple subscription with all billing centralized just as it is today.
-
Upgrade: Red Hat provides a published product life cycle for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in order for customers and partners to effectively plan, deploy, and support their applications running on the platform. Red Hat publishes this life cycle in order to provide as much transparency as possible and might make exceptions from these policies as conflicts arise.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS is a managed instance of Red Hat OpenShift and maintains an independent release schedule. The availability of Security Advisories and Bug Fix Advisories for a specific version are dependent upon the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform life cycle policy and subject to the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS maintenance schedule.
-
-
Red Hat Openshift Cluster Manager:
-
Red Hat OCM: Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager is a managed service where you can install, modify, operate, and upgrade your Red Hat OpenShift clusters. This service allows you to work with all of your organization’s clusters from a single dashboard.
OpenShift Cluster Manager guides you to install OpenShift Container Platform, Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA), and OpenShift Dedicated clusters. It is also responsible for managing both OpenShift Container Platform clusters after self-installation as well as your ROSA and OpenShift Dedicated clusters. You can use OpenShift Cluster Manager to do the following actions:
-
Create new clusters
-
View cluster details and metrics
-
Manage your clusters with tasks such as scaling, changing node labels, networking, authentication
-
Manage access control
-
Monitor clusters
-
Schedule upgrades
-
-
6. The story behind this solution pattern
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) is for customers who want an OpenShift experience in AWS with close integration to AWS services, joint support, and a single bill. It helps ensure consistency across environments and is jointly managed and supported by Red Hat and AWS. It can be purchased directly through the AWS console and offers pay-as-you-go, single-vendor invoicing. Its key differentiators:
-
Built for the hybrid cloud
-
Public cloud, on-premise, or at the edge.
-
Centralized management that spans across hosting environments.
-
-
Complete, hardened, and supported platform for modern applications
-
Whole-product solution integrating all tools required for the full software development life cycle.
-
Range of metering, monitoring, and observability capabilities.
-
-
Broad open source and ISV ecosystem
-
Supported and deployed through the OpenShift Operator Framework with a choice of toolsets to help automate and integrate operations.
-
7. The Solution
This solution pattern demonstrates different features of Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS and how well it integrates with different AWS services. In this pattern, we will look at ROSA’s architecture with public/private network as well as with AWS PrivateLink. At the end, we will deploy an application(OSToy) and perform various activities on this application as part of the workshop to demonstrates how easy it is work with ROSA.
8. Explore more solution patterns
404: Not Found